[post-views]
In this lesson, you will learn.
- What is AWT
- What is Swing
- Advantages of using Swing Over AWT
- Key differences b/w AWT and Swings
- Component Hierarchy of Swing Component
What is AWT in Java?
- AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) is a part of the Java Foundation Classes (JFC) used to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for Java applications.
- AWT provides a set of APIs for creating and managing windows, buttons, text fields, and other GUI components.
- It is a platform-dependent API, meaning that the look and feel of the components can vary between different operating systems.
- The AWT classes are contained in the java.awt package.
To solve this problem(i.e. platform dependent), Java upgrades and extends the original components through the Swing toolkit.
What is Swing in Java?
Swing is a part of the Java Foundation Classes (JFC) and provides a more powerful and flexible GUI toolkit than AWT.
Here are the advantages of using Swing over AWT, followed by a table highlighting key differences between the two.
Advantages of Using Swing Over AWT
- Platform Independence:
- Swing components are written entirely in Java and are platform-independent.
- They have a consistent look and feel across different operating systems.
- Pluggable Look and Feel:
- Swing supports pluggable look-and-feel, allowing developers to change the appearance of applications dynamically.
- This means you can use a cross-platform look and feel or one that mimics the native OS.
- Rich Set of Components:
- Swing provides a richer set of GUI components than AWT.
- It includes advanced components like trees, tables, tabbed panes, sliders, and more.
- Customizable Components:
- Swing components are highly customizable.
- You can easily create your own components by extending existing ones.
- Lightweight Components:
- Unlike AWT, which relies on native code (heavyweight components), Swing components are lightweight as they do not rely on native peers.
- This leads to better performance and flexibility.
- MVC Architecture:
- Swing uses the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, which separates the data (model), the UI (view), and the control logic (controller).
- This separation allows for more modular and maintainable code.
Key Differences Between AWT and Swing
| Feature |
AWT |
Swing |
| Look and Feel |
Platform-dependent (native look) |
Pluggable look-and-feel (consistent across platforms) |
| Components |
Basic set of components |
Rich set of advanced components |
| Customizability |
Limited customization |
Highly customizable |
| Component Type |
Heavyweight (rely on native peers) |
Lightweight (purely Java) |
| Event Handling |
Old event handling model |
Improved event handling with delegation |
| Thread Safety |
Not thread-safe |
Not thread-safe, but provides SwingUtilities.invokeLater for thread safety |
| MVC Architecture |
No explicit support for MVC |
Built-in support for MVC architecture |
| Performance |
Dependent on native system performance |
Generally better performance due to the lightweight nature |
| Appearance |
Native appearance |
Consistent appearance, can mimic native or custom looks |
| Dependencies |
Uses native OS components |
Pure Java implementation |
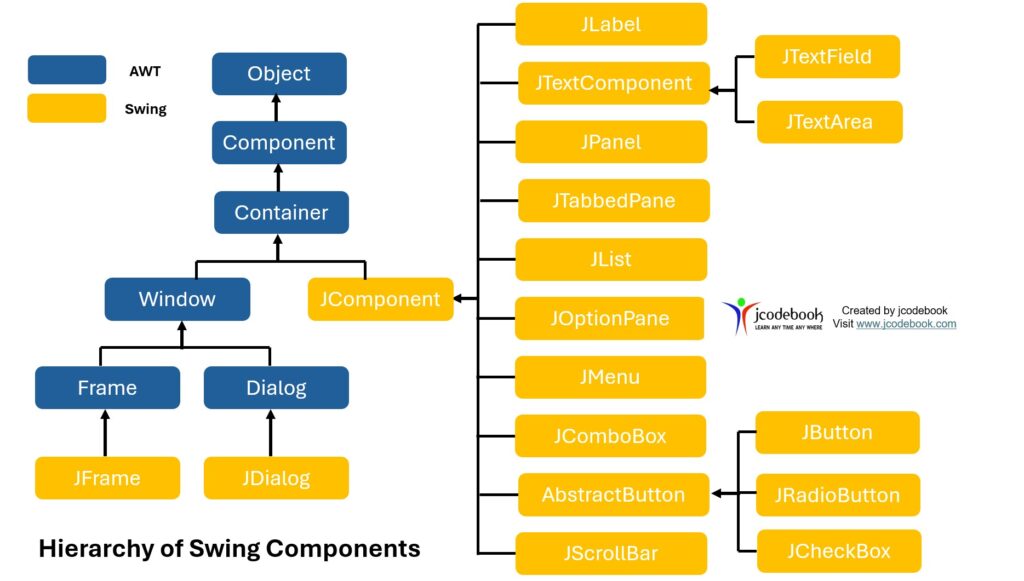
Hierarchy of Swing Component
The following figure shows the hierarchy of Swing components.
End of the lesson….enjoy learning
Student Ratings and Reviews
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.
Submit a Review