In this lesson, you will learn
Polymorphism is the ability of a single entity, such as a function, object, or operator, to take on multiple forms or behaviors depending on the context.
It allows the same action or method to be applied in different ways based on the data type, object, or parameters involved.
Imagine you have a remote control (like a universal remote) that can operate multiple devices: a TV, a DVD player, and a sound system. The remote has a single button labeled “Play.”
In this analogy, the remote control is the common interface, and “Play” is the function. Each device (TV, DVD player, sound system) has a different way of responding to the same “Play” command, which represents different implementations in separate classes. The remote control doesn’t need to know how each device works internally; it just sends the command.
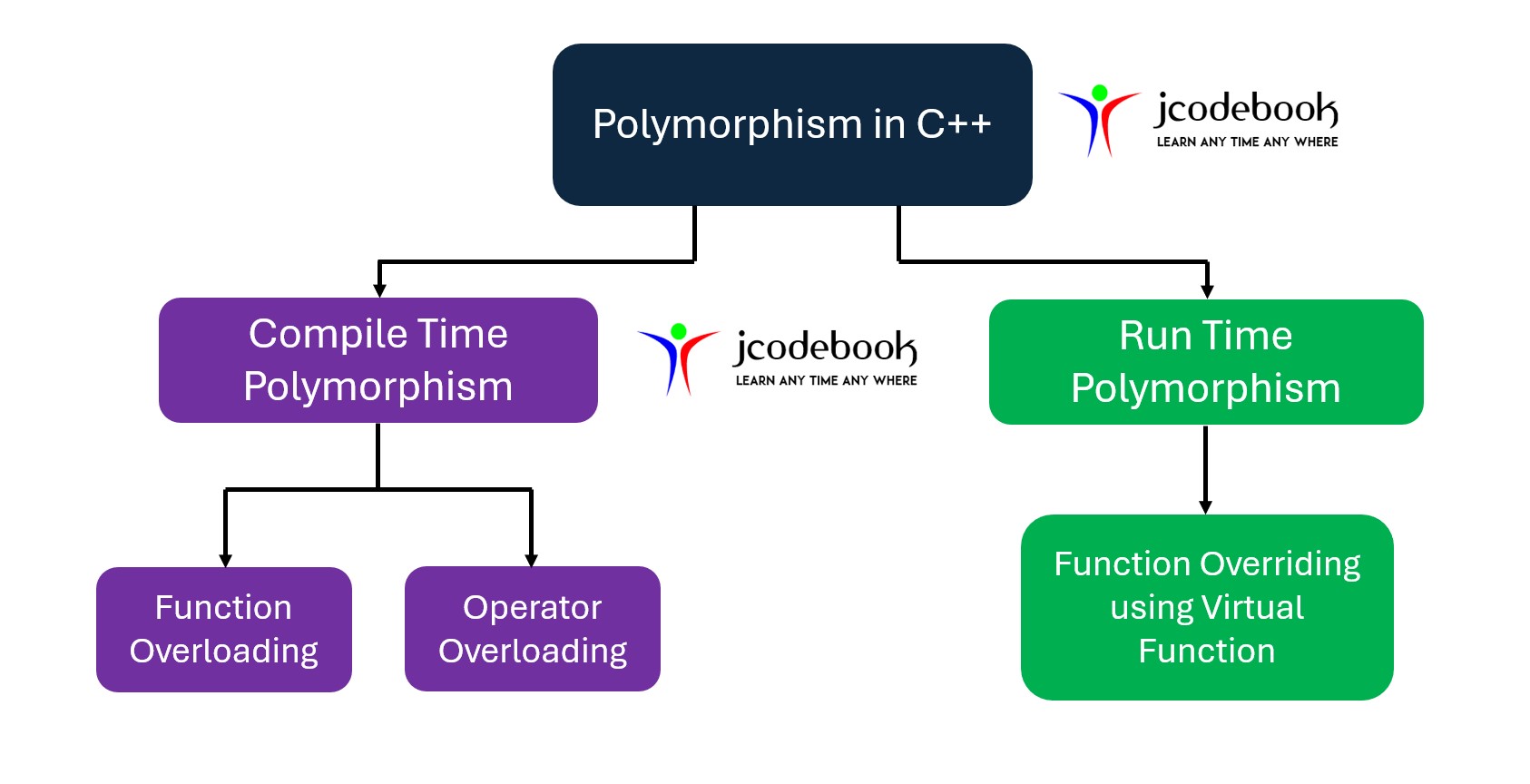
Compile-time Polymorphism (Static Polymorphism): The function to be called is determined at compile time. This is achieved through:
+, -, etc.).Run-time Polymorphism (Dynamic Polymorphism): The function to be executed is determined at runtime. This is achieved through:
Runtime Polymorphism will be discussed in the Inheritance Chapter.
To implement the remote control example using function overloading with a single class, we can define a Device class that has overloaded methods to handle different types of devices (TV, DVD player, sound system). We’ll simulate the different devices by passing either different types of arguments or different constants to the overloaded methods.
Here is an example using a single class:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Single class for Remote
class Remote {
public:
// Overloaded play() function for different device types
// Function for playing TV
void play(int deviceType) {
if (deviceType == 1) {
cout << "Playing TV channel." << endl;
}
else if (deviceType == 2) {
cout << "Playing DVD." << endl;
}
else if (deviceType == 3) {
cout << "Playing music on Sound System." << endl;
}
else {
cout << "Invalid device type." << endl;
}
}
// Function for adjusting volume
void play(double volumeLevel) {
cout << "Adjusting volume to level: " << volumeLevel << endl;
}
// Function for media type input (TV, DVD, Music)
void play(string mediaType) {
if (mediaType == "TV") {
cout << "Playing TV media." << endl;
}
else if (mediaType == "DVD") {
cout << "Playing DVD media." << endl;
}
else if (mediaType == "Music") {
cout << "Playing music media." << endl;
}
else {
cout << "Invalid media type." << endl;
}
}
};
int main() {
Remote remote;
// Playing different devices using device type (int)
remote.play(1); // Output: Playing TV channel.
remote.play(2); // Output: Playing DVD.
remote.play(3); // Output: Playing music on Sound System.
// Adjusting volume using a different overloaded method
remote.play(9.5); // Output: Adjusting volume to level: 9.5
// Playing media using media type (string)
remote.play("TV"); // Output: Playing TV media.
remote.play("DVD"); // Output: Playing DVD media.
remote.play("Music"); // Output: Playing music media.
return 0;
}
Playing TV channel.
Playing DVD.
Playing music on Sound System.
Adjusting volume to level: 9.5
Playing TV media.
Playing DVD media.
Playing music media.
Single Remote Class: The Remote class contains three overloaded play() functions:
int) to represent the device type (1 for TV, 2 for DVD player, 3 for Sound System).double) to represent volume adjustment.string) to represent the media type (e.g., “TV”, “DVD”, “Music”).In main():
play() method is called with different types of arguments (int, double, string), and the appropriate version of the overloaded function is executed based on the argument type.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// TV class
class TV {
public:
void play() { // Overloaded function for TV
cout << "Playing TV channel." << endl;
}
};
// DVD Player class
class DVDPlayer {
public:
void play() { // Overloaded function for DVDPlayer
cout << "Playing DVD." << endl;
}
};
// Sound System class
class SoundSystem {
public:
void play() { // Overloaded function for SoundSystem
cout << "Playing music." << endl;
}
};
// Remote class
class Remote {
public:
// Overloaded play() function for each device type
void play(TV& tv) {
tv.play();
}
void play(DVDPlayer& dvd) {
dvd.play();
}
void play(SoundSystem& sound) {
sound.play();
}
};
int main() {
TV tv;
DVDPlayer dvd;
SoundSystem sound;
Remote remote;
// Using function overloading to control different devices
remote.play(tv); // Output: Playing TV channel.
remote.play(dvd); // Output: Playing DVD.
remote.play(sound); // Output: Playing music.
return 0;
}
Playing TV channel.
Playing DVD.
Playing music.
clear and concise explanation
You must be logged in to submit a review.